Spring Boot中的异步方法调用
在Spring Boot中,异步方法调用是通过@Async注解实现的。这个注解可以将一个同步方法转换为异步执行,即在不同的线程中运行。这样做的好处是可以提高应用程序的性能,特别是在处理耗时任务时,可以避免阻塞主线程。
使用@Async注解
要在Spring Boot中使用 @Async 注解,首先需要在启动类上添加 @EnableAsync 注解来启用异步支持。然后,可以在需要异步执行的方法上添加 @Async 注解。例如:
@Service
public class AsyncService {
@Async
public void asyncMethod() {
// 异步执行的代码
}
}这个方法现在会在单独的线程中异步执行。如果方法有返回值,可以使用Future接口来处理异步结果。例如:
@Service
public class AsyncService {
@Async
public Future<String> asyncMethodWithReturn() {
// 异步执行的代码
return new AsyncResult<>("结果");
}
}自定义线程池
默认情况下,@Async注解会使用SimpleAsyncTaskExecutor作为线程池。但是,这个默认的线程池对于生产环境通常不是最佳选择,因为它会为每个任务创建一个新线程。因此,推荐自定义线程池来优化性能和资源使用。可以通过实现AsyncConfigurer接口并重写getAsyncExecutor方法来自定义线程池。例如:
@Configuration
@EnableAsync
public class AsyncConfig implements AsyncConfigurer {
@Override
public Executor getAsyncExecutor() {
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor();
executor.setCorePoolSize(10);
executor.setMaxPoolSize(50);
executor.setQueueCapacity(100);
executor.initialize();
return executor;
}
}在这个配置中,定义了一个核心线程数为10,最大线程数为50,队列容量为100的线程池。这样配置后,@Async注解就会使用这个自定义的线程池来执行任务。
异步方法的限制
使用 @Async 注解时,有一些限制需要注意:
- 异步方法不能是static方法。
- 异步方法所在的类必须被Spring容器管理,即通过 @Component 或其他相关注解声明。
- 异步方法不能和调用它的方法在同一个类中。
- 类中的依赖必须通过 @Autowired 或 @Resource 等注解自动注入,不能手动创建对象。
- 如果使用Spring Boot框架,必须在启动类中添加 @EnableAsync 注解。
- 在异步方法上标注 @Transactional 是无效的,应该在调用异步方法的方法上标注。
默认线程与自定义线程池
SimpleAsyncTaskExecutor 的特点
- 非池化:
SimpleAsyncTaskExecutor不是一个真正的线程池,它每次都会创建一个新的线程来执行任务。 - 无限创建线程:如果没有限制,它会无限创建新线程,这可能导致资源耗尽。
- 不会自动关闭:
SimpleAsyncTaskExecutor不会自动关闭其创建的线程,因为它是基于简单的线程创建机制,而不是线程池。
测试代码
AynscController
/**
* @Author: xxl
* @Date: 2024/11/22 15:17
*/
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/aynsc")
public class AynscController {
@Autowired
private AynscService aynscService;
@GetMapping("/testAynsc")
public String testAynsc() {
for (int i = 1; i <= 100; i++) {
aynscService.sendAynscMessage(i);
}
return "执行成功";
}
}AynscService
/**
* @Author: xxl
* @Date: 2024/11/22 15:17
*/
@Component
public class AynscService {
@Async
public void sendAynscMessage(Integer index) {
System.out.println("发送异步消息,第" + index + "次!");
}
}SimpleAsyncTaskExecutor
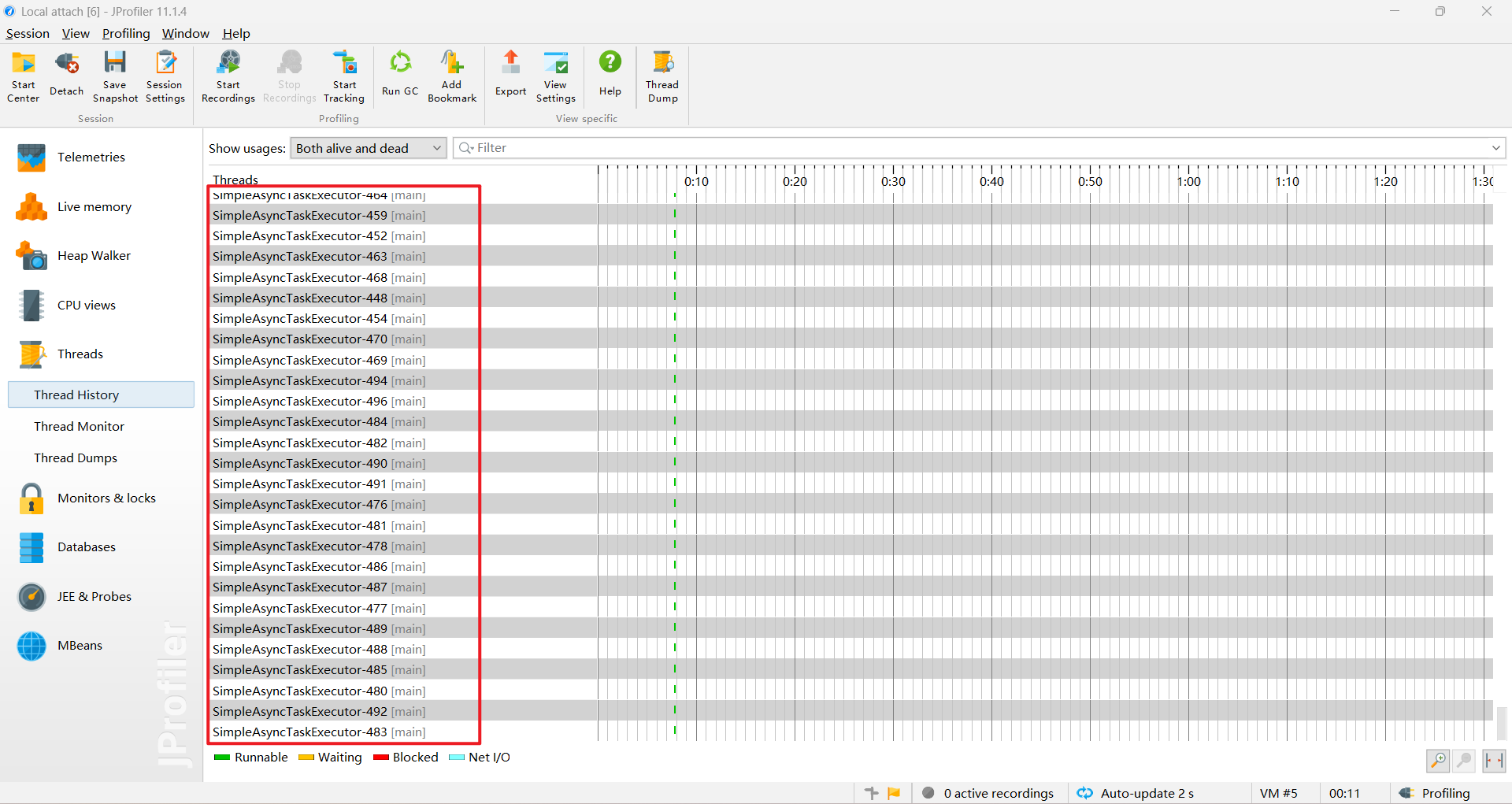
添加自定义线程池
/**
* 自定义线程池
*
* @Author: xxl
* @Date: 2024/11/22 15:38
*/
@Configuration
public class AsyncConfig {
@Bean
public ThreadPoolTaskExecutor taskExecutor() {
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor();
executor.setCorePoolSize(4); // 核心线程数
executor.setMaxPoolSize(8); // 最大线程数
executor.setQueueCapacity(100); // 队列容量
executor.setThreadNamePrefix("async-thread-"); // 线程名称前缀
executor.initialize();
return executor;
}
}或
/**
* @Author: xxl
* @Date: 2024/11/22 16:14
*/
@Configuration
@EnableAsync
public class AsyncConfig2 implements AsyncConfigurer {
@Override
public Executor getAsyncExecutor() {
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor();
executor.setCorePoolSize(5);
executor.setMaxPoolSize(10);
executor.setQueueCapacity(25);
executor.setThreadNamePrefix("Async-");
executor.initialize();
return executor;
}
}自定义线程池
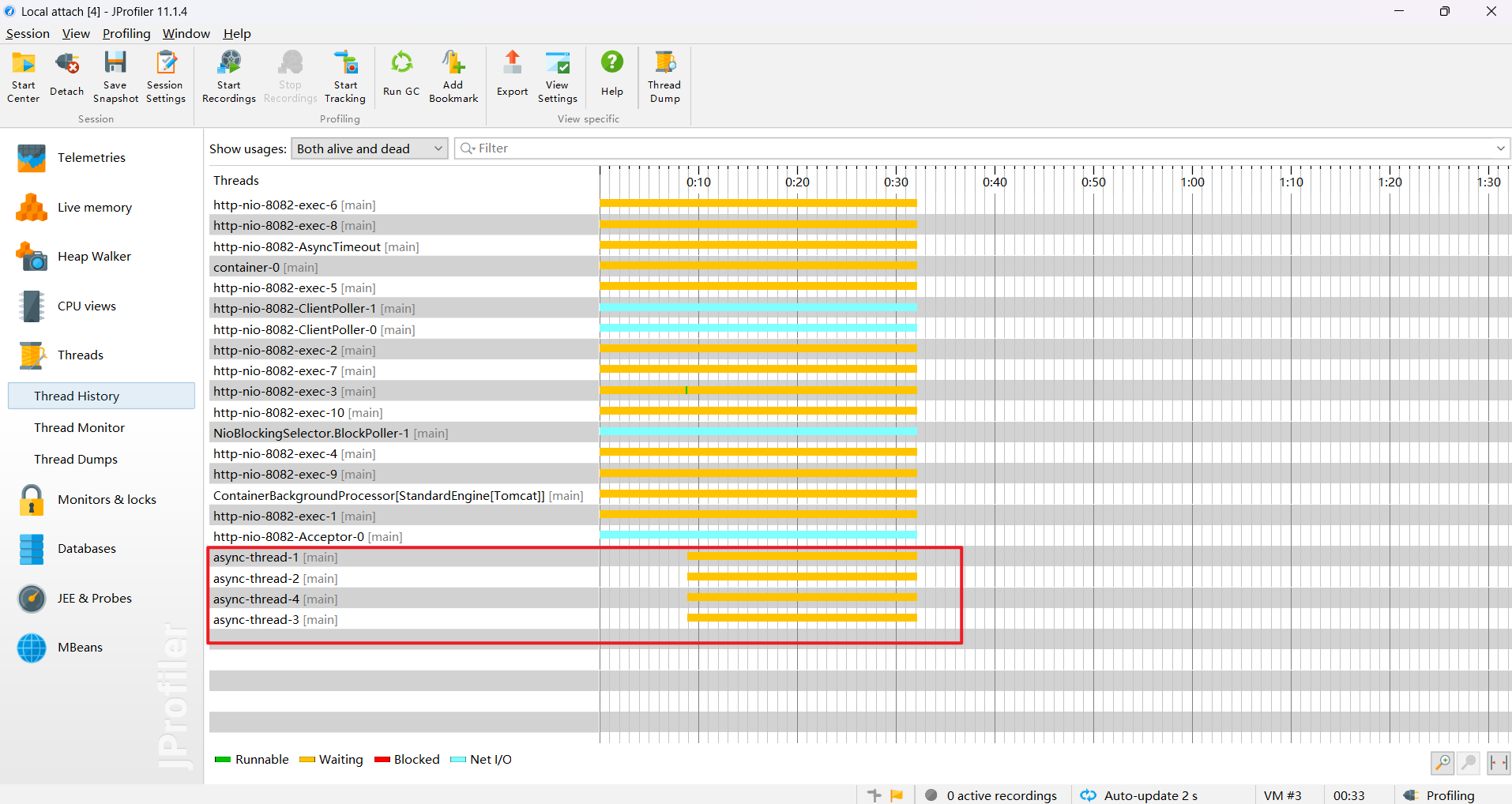
获取源码可访问
springboot_chowder/springboot_aynsc at main · Daneliya/springboot_chowder
总结
@Async注解提供了一种简单而强大的方式来实现异步方法调用,可以显著提高应用程序的性能。通过自定义线程池,可以进一步优化资源使用和控制异步任务的执行。在使用时,需要注意一些限制条件,以确保异步调用能够正确执行。
